Muoversi meglio, vivere meglio
Il Parkinson ti toglie la sicurezza, Gondola ti restituisce la libertà
La terapia Gondola AMPS stimola specifici punti dei tuoi piedi per riattivare le aree cerebrali che controllano movimento ed equilibrio. Una stimolazione meccanica, precisa, non invasiva, che in soli 2 minuti incrementa la sicurezza nel cammino e migliora la tua vita e quella dei tuoi cari.
SCOPRI GONDOLA IN 1 MINUTO

Cos'è Gondola AMPS
La terapia Gondola AMPS è stata ideata per un utilizzo regolare e continuativo, ed è compatibile con i trattamenti già in corso.
Consiste in un trattamento di 2 minuti che applica pressioni precise in due punti specifici di entrambi i piedi.
Questa stimolazione contribuisce a riattivare aree cerebrali coinvolte nella gestione del cammino e dell’equilibrio.
Si tratta di un metodo scientificamente validato, testato su migliaia di pazienti in più di 10 anni. Esiste un modo per convivere con il Parkinson e condurre una vita soddisfacente nonostante la malattia: puoi sperimentarlo direttamente provando il dispositivo Gondola in uno dei nostri centri partner.
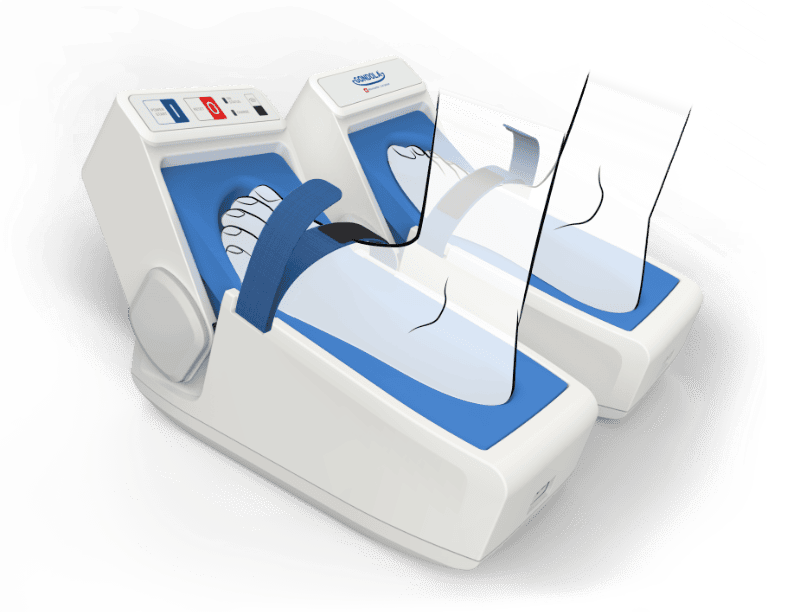
I vantaggi di Gondola
Gondola rappresenta un importante avanzamento nel trattamento dei sintomi motori causati dal Parkinson, offrendo una soluzione rapida, non invasiva e supportata da studi scientifici.
Veloce
Migliori subito
Non fa male
Gondola ti cambia la vita!
Noterai fin da subito un miglioramento nel cammino, nell’equilibrio e una maggiore stabilità.
Cammini meglio
Meno cadute, più sicurezza
Camminare torna naturale
Chi utilizza Gondola non ha dubbi
Non c’è miglior testimonial di chi beneficia di Gondola e vive ogni giorno una vita più libera dalle restrizioni del Parkinson.




Gli studi clinici
Gondola Medical Technologies si è sempre impegnata a produrre prove scientifiche sull’efficacia della terapia Gondola AMPS. La sicurezza e l’efficacia della terapia sono state documentate in studi di ricerca clinica su oltre 300 pazienti affetti da malattia di Parkinson.
Gli studi hanno indicato che con l’uso regolare si può osservare un aumento della velocità di cammino, un tempo più rapido nel test “timed up-and-go” (TUG), un incremento della lunghezza del passo, una marcia più simmetrica e una migliore capacità di invertire la direzione, segno di miglioramenti nell’equilibrio dinamico.
Le ricerche sulla terapia Gondola AMPS continuano nel tempo, con l’obiettivo di approfondire e comprendere appieno il suo potenziale nei pazienti con malattia di Parkinson e altre patologie neurologiche.
Parliamo di Parkinson
Approfondimenti e risorse per chi vive quotidianamente con il Parkinson




